Does Chlorine Kill Molluscum Contagiosum

Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection that causes small, flesh-colored bumps. The bumps are usually round and have a dimple in the center. They may be pink, white, or yellow.
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus. The virus is spread through direct contact with an infected person or object. It can also be spread through sexual contact.
The bumps usually appear 2 to 8 weeks after exposure to the virus.
WART POPS OUT OF FOOT! AMAZING WART REMOVAL!
If you’re looking for a way to treat molluscum contagiosum, you may have heard that chlorine can be effective. But does chlorine actually kill the virus that causes this condition?
The answer is yes, chlorine can kill the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV).
In fact, it’s one of the most effective treatments for this condition. When applied to the affected area, chlorine will destroy the virus and help to heal the skin.
There are a few different ways to use chlorine to treat molluscum contagiosum.
You can either soak a cotton ball in chlorinated water and apply it to the affected area, or you can add chlorinated water to a bath and soak in it for 20 minutes. Whichever method you choose, make sure you do not rinse off the chlorine until after 20 minutes have passed.
If you’re looking for an effective way to treat molluscum contagiosum, give chlorine a try!
Molluscum Contagiosum Stages Pictures
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection that is caused by a virus. The virus causes raised, flesh-colored bumps to form on the skin. The bumps are usually round and have a dimple in the center.
They are generally found on the face, chest, back, stomach, arms, legs, or genital area. Molluscum contagiosum is contagious and can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or by sharing contaminated objects such as towels or clothing. The infection is most commonly seen in children but can occur in adults as well.
There is no cure for molluscum contagiosum but it will eventually go away on its own over time. Treatment options are available to help speed up the healing process and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to others.
Does Hand Sanitizer Kill Molluscum
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection that is caused by a virus. The virus can be spread through direct contact with an infected person or through contact with contaminated surfaces. The infection causes small, raised bumps on the skin that are usually flesh-colored.
The bumps may be itchy or sore. Molluscum contagiosum is most common in children and young adults, but it can occur in people of any age. There is no cure for molluscum contagiosum, but it usually goes away on its own within 6 to 12 months.
In some cases, the bumps may persist for years.
There are several treatments that can be used to speed up the healing process and reduce the number of bumps. One treatment option is to apply a topical cream or ointment to the affected area.
This will help to dry out the bumps and cause them to eventually fall off. Another option is cryotherapy, which involves freezing the bumps with liquid nitrogen. This treatment can be painful and may cause scarring.
If you have molluscum contagiosum, it’s important to avoid touching or scratching the bumps, as this can spread the virus to other parts of your body or to other people.
Does Chlorine Kill Monkeypox
Chlorine is a powerful disinfectant that is used to kill harmful bacteria and viruses. It is also effective against monkeypox, a disease that is similar to smallpox. Monkeypox is a serious illness that can be deadly, so it is important to take steps to prevent the spread of the disease.
Chlorine can help to kill the virus that causes monkeypox, and it can also help to prevent the disease from spreading.
Does Chlorine Kill Chickenpox Virus
Chlorine does not kill chickenpox virus. However, it can help to prevent the spread of the virus by reducing the amount of time that the virus can survive on surfaces. This is why it is important to keep pool areas clean and free of debris.
Molluscum Contagiosum Kids
Molluscum contagiosum is a highly contagious skin condition that most often affects kids. It’s caused by a virus and can spread quickly through close contact with someone who has it or through sharing contaminated items like towels or clothing. The good news is that molluscum contagiosum is usually a benign and self-limited condition that will eventually go away on its own.
In the meantime, there are several treatment options available to help speed up the healing process and relieve any discomfort.
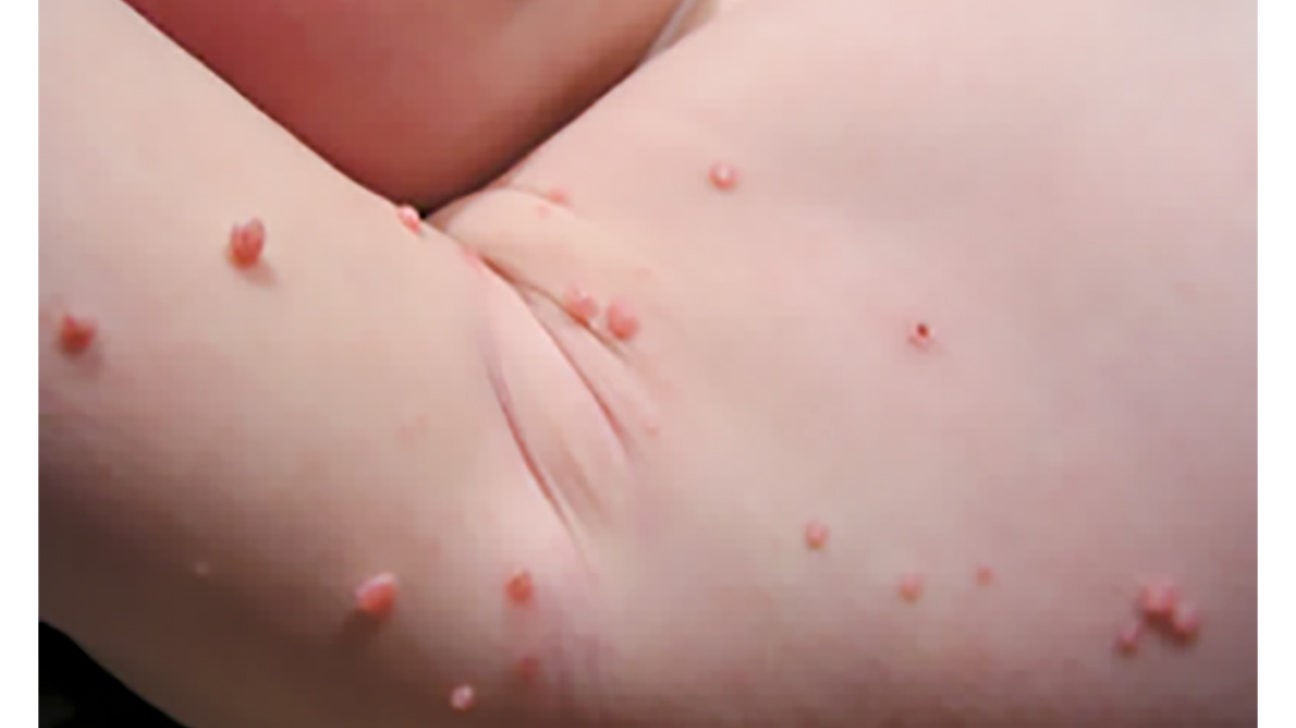
Credit: www.healthline.com
Can You Swim in a Pool With Molluscum Contagiosum?
Yes, you can swim in a pool with molluscum contagiosum. The virus that causes molluscum contagiosum is not spread through water, so swimming in a pool will not put you at risk for contracting the virus. However, it is possible to spread the virus to others through close contact, so it is important to take precautions to avoid infecting others.
Covering your lesions with a bandage or wearing loose-fitting clothing can help prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum.
Can Kids Go Swimming With Molluscum?
Molluscum contagiosum is a skin infection that is caused by a virus. The virus can spread through direct contact with an infected person or through contact with contaminated objects. Molluscum contagiosum is most common in children, but it can occur in adults as well.
The infection usually causes small, raised bumps on the skin. These bumps may be flesh-colored, pink, white, or yellow. They are usually not painful or itchy.
In most cases, molluscum contagiosum goes away on its own within 6 to 12 months. However, the virus can remain active for years and cause new outbreaks of the infection.
There is no specific treatment for molluscum contagiosum.
However, there are several ways to reduce the risk of spreading the infection:
-Avoiding direct contact with an infected person
-Washing your hands thoroughly after touching an infected person or object
-Not sharing personal items (towels, clothing) with an infected person
-Keeping any cuts or scrapes clean and covered with a bandage until they heal
Can kids go swimming with molluscum?
There is no definitive answer as to whether or not kids can swim with molluscum contagiousm since there is no known cure for the virus. However, because the virus can be spread through direct contact, it is generally recommended that kids refrain from swimming if they have molluscum contagiousm or if they have been in close contact with someone who does.
What Kills the Molluscum Virus?
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection that causes small, flesh-colored bumps. The bumps are usually painless and do not cause any other symptoms. They often occur in clusters and can spread from one person to another through close contact.
Molluscum contagiosum is most common in children, but it can affect people of any age. There is no cure for the virus, but it usually goes away on its own within 6 to 12 months. In some cases, the bumps may persist for longer periods of time.
Treatment is typically not necessary unless the bumps are causing discomfort or spreading to other areas of the body. There are several treatments that can be used to remove the bumps, including cryotherapy, laser therapy, and topical creams.
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a virus in the poxvirus family.
The virus is spread through direct contact with an infected person or object. It can also be spread indirectly through contact with contaminated surfaces, such as towels or clothing. The virus can also be transmitted sexually.
Once contracted, the virus causes mollusca (singular: molluscum), which are small flesh-colored bumps that often occur in clusters on the skin surface. The bumps are usually Painless But Can Be Pruritic (itchy). They range in size from 2 mm to 5 mm and have a central depression that contains a core of white material known as molluscogenic material or virions.
Mollusca typically appear 2-8 weeks after exposure to the virus and often resolve spontaneously within 6-12 months without treatment; however, they may persist for years in some individuals
There is currently no cure for molluscum contagiosum and no vaccine available to prevent its spread. Treatment is typically only necessary if the condition is causing discomfort or spreading to other areas of the body.
Can Molluscum Contagiosum Spread in a Hot Tub?
Molluscum contagiosum, or MC, is a highly contagious skin condition caused by a virus. The virus that causes MC is called the molluscipoxvirus, and it can spread through close contact with an infected person or through contact with contaminated surfaces.MC can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in children. The virus can spread quickly in places where there are close physical contacts, such as daycare centers, schools and swimming pools.
In addition, hot tubs can also be a source of viral transmission if they are not properly cleaned and disinfected between uses.
The symptoms of MC include small bumps on the skin that are usually flesh-colored or white. These bumps can appear anywhere on the body, but they are most commonly found on the face, neck, chest, stomach or arms.
The bumps may be itchy or sore, but they are usually painless.MC is generally not harmful and will eventually go away on its own without treatment; however, the condition can last for months or even years in some cases. There are several treatments available that can speed up the healing process and help to reduce the risk of spreading the virus to others.
If you think you have MC, it is important to see a doctor so that you can get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment if necessary.
It is also important to practice good hygiene and avoid sharing personal items with others to help prevent the spread of infection.
Conclusion
Chlorine does not kill molluscum contagiosum. This virus is highly contagious and can be passed through skin-to-skin contact, sexual contact, or sharing infected items. The virus causes small, raised bumps on the skin that are usually flesh-colored.
These bumps can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, chest, stomach, thighs, or genitals. There is no cure for molluscum contagiosum and it can take up to two years for the bumps to go away on their own. Treatment options are available to help speed up the healing process and prevent the virus from spreading.

